Database Indexes¶
Resources¶
Why indexing¶
- Faster reads and queries
- slow queries are a common reason why websites are slow
- slow websites -> less profit
Analogy for index¶

like tabs of a nice dictionary
links to the page, has no other info other than the first letter
Key vs Index¶
Index: data structure
- keys aren't necessarily indexed
- example: all the column fields form a key
- key: list of columns that uniquely identify any row
Primary key is always indexed
What an index looks like¶
b-tree!
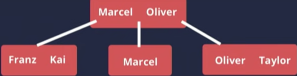
It will only have the data in the index
Downsides of an index¶
Downside to database indices
- Work to maintain the index 2. reads are slower 3. or you have to defrag/reindex
- CREATE INDEX is expensive
- especially on a large table
- Extra space 4. b trees and hash tables 5. some indexes can be huge, especially if the table is huge
Secondary indexing¶
Student(year, major)
sort by birthday
useful if your queries are like
Not useful if you have a query like
Data not sorted wrt secondary index
so it has to do a sequential scan
Date indexes¶
Problem with this query
Table is indexed on created_at
can't use created_at index because it's only indexed on the raw dates
psql solution¶
create an index on YEAR(created_at)
non psql solution¶
Types of indexes¶
Cluster index????
Last update:
2023-04-24